The Road to Optimal Health
ENT Consultant & Laryngologist
🔷 14 years of experience
🔷 Subspecialty in Voice Disorders and Vocal Cord Treatment
🔷 Located in Al Ain, Abu Dhabi
See my services below 👇
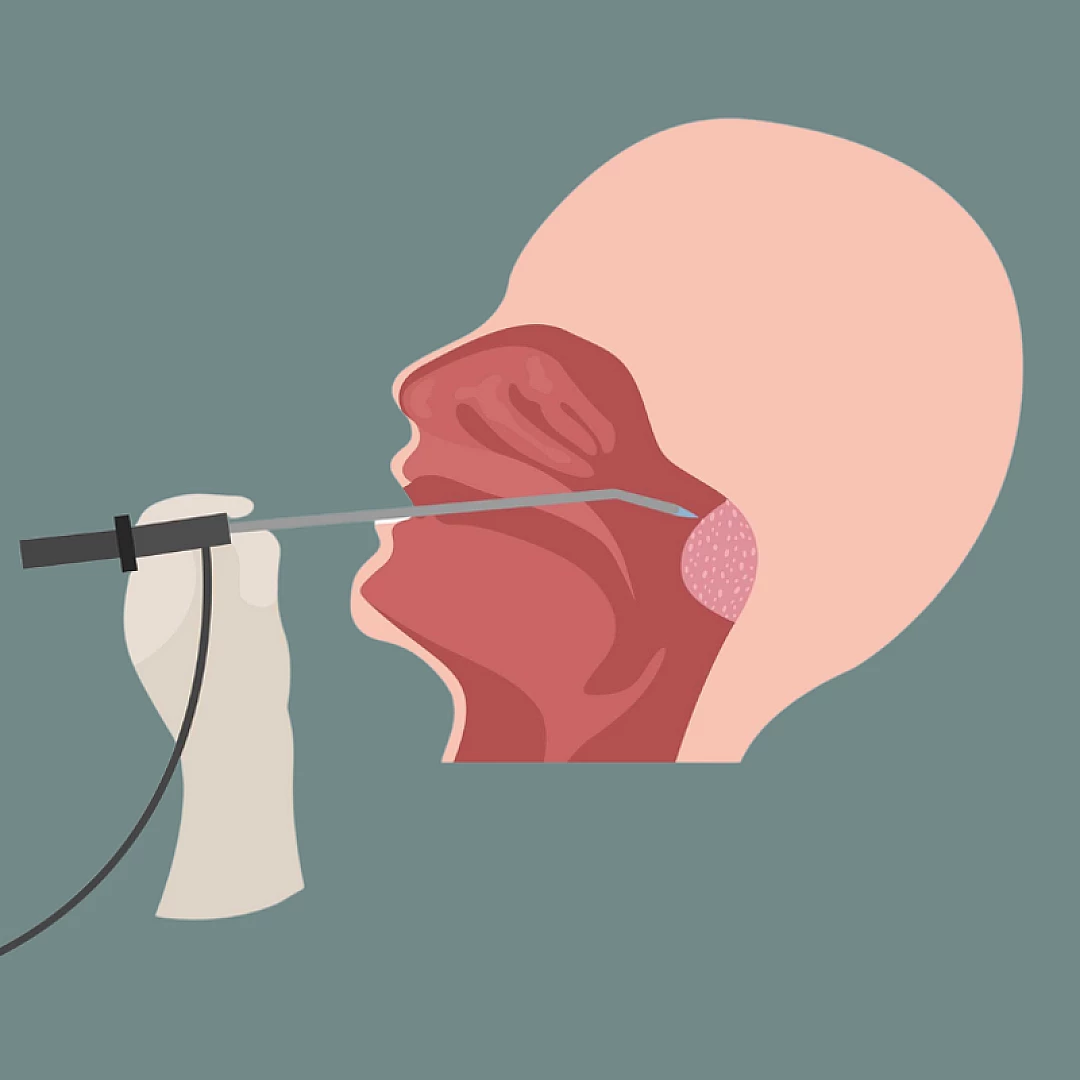
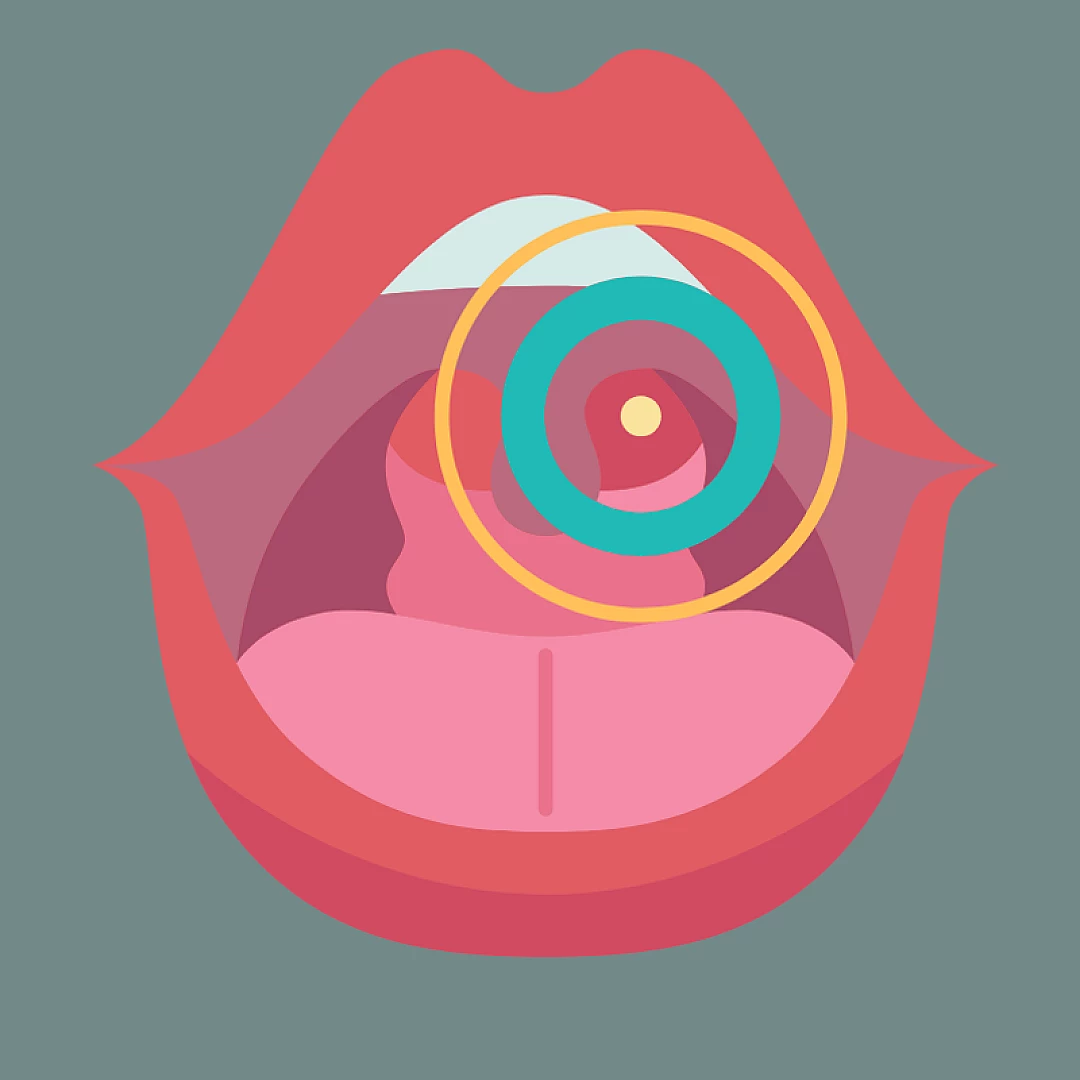
Vocal Cord Nodules
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Symptoms include hoarseness, and if the nodule is large, it may cause breathing difficulties
- Treatment is surgical, using endoscopy and laser techniques
- The patient requires voice therapy exercises before and after the procedure
Laryngeal and Vocal Cord Cancer
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Laryngospasm is a temporary contraction of the vocal cords that can be treated, making it difficult to speak or breathe for a short period
- Effective treatment depends on accurate diagnosis
- Therapy includes voice exercises to aid in recovery
- Multiple sessions may be required for improvement
- The condition can be treated with Botox injections, either under local anesthesia in the clinic or general anesthesia in the operating room
- Patients need to repeat Botox injections approximately every six months or when bothersome symptoms reappear
Throat Cancer and Vocal Cords
Diagnosis and Treatment
- Diagnosis is performed using endoscopy
- A CT scan or MRI may be required, depending on the tumor size
- A biopsy is necessary for further examination
- Treatment depends on the cancer stage
- Treatment options include tumor removal via endoscopy, radiation therapy, or, in rare cases, total laryngectomy
- After treatment, regular follow-up visits are essential
Laryngeal Papillomas
Accurate Diagnosis
- Recurrent respiratory papillomatosis is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV)
- It leads to hoarseness, breathing difficulties, and airway obstruction if the tumor is large
- These tumors rarely develop into cancerous growths
- Tumors are removed using laser surgery
- Regular procedures may be required, as the growth can recur after removal
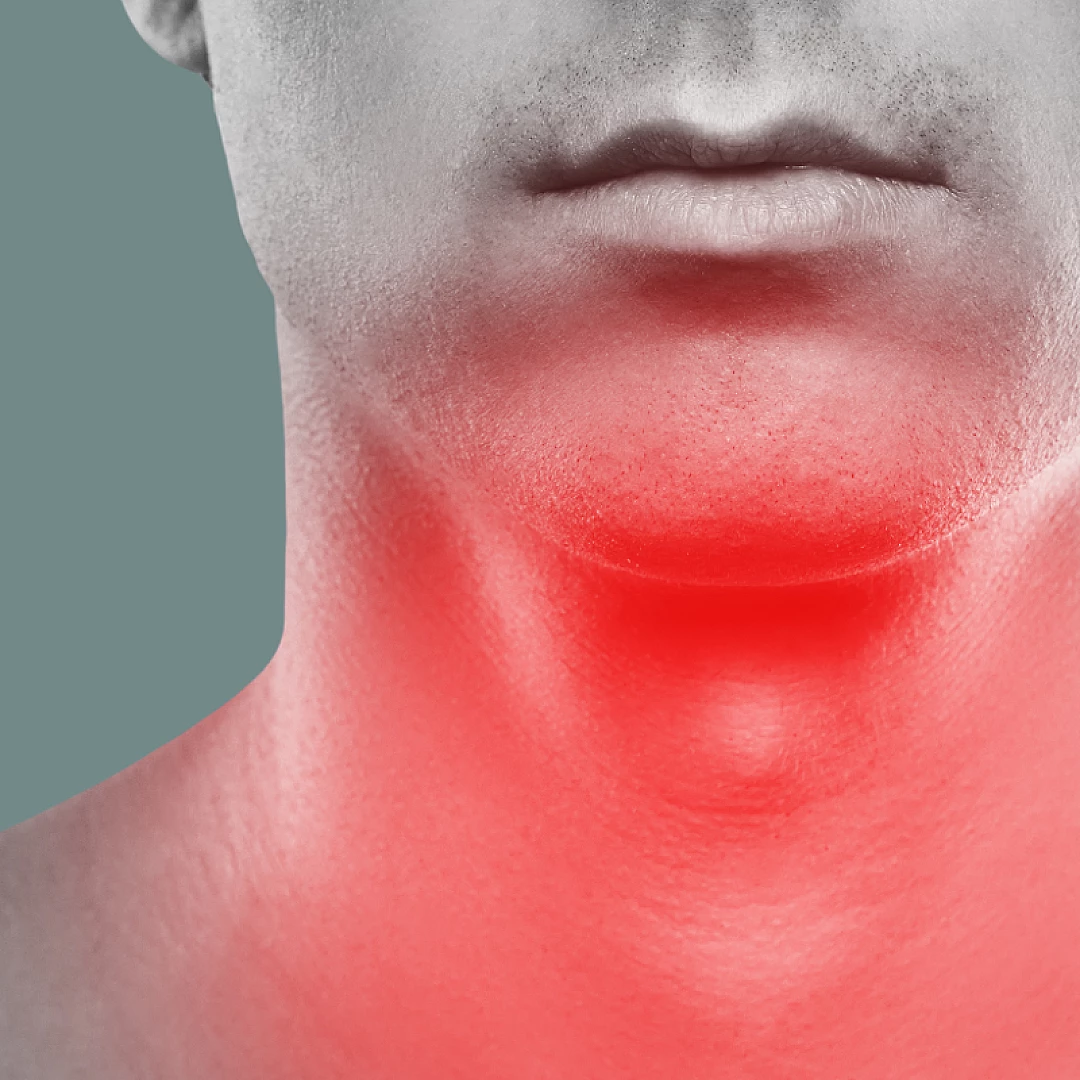
Hoarseness
Diagnosis and Treatment
Hoarseness is diagnosed through:
- Medical history assessment and voice evaluation
- Laryngoscopy and vocal cord examination in the clinic
- Treatment depends on the underlying diagnosis
Vocal Cord Paralysis
Diagnosis and Treatment
Symptoms of Vocal Cord Paralysis Include:
- Breathy voice, hoarseness, noisy breathing, weakened voice, choking or coughing while swallowing
- Frequent need to breathe while speaking, inability to speak loudly, or weak cough
Causes of Vocal Cord Paralysis:
- Nerve injury after thyroid or neck surgery
- Viral infections, stroke, or brain damage affecting nerve signals to the larynx
Diagnosis Includes:
- Medical history review, voice assessment, laryngoscopy, and laryngeal electromyography
- In some cases, MRI, CT scans, or blood tests may be required to determine the cause
Treatment Options:
- Voice therapy sessions and vocal exercises
- Injection medialization, structural implants, nerve reinnervation
- Laser surgery to remove part of the vocal cord for airway widening
Acid Reflux
Diagnosis and Treatment
Symptoms Include:
- Hoarseness, cough, chest pain, choking sensation
- Feeling of a foreign body in the throat, difficulty swallowing, and heartburn
Diagnosis:
- Medical history assessment and laryngoscopy to examine the larynx and vocal cords
Treatment:
- Lifestyle and dietary modifications
- Medication as prescribed
- In severe cases, consultation with a gastroenterologist is recommended
Subglottic Stenosis
Diagnosis and Treatment
A congenital or acquired airway narrowing below the vocal cords (subglottis).
Symptoms include:
- Breathing difficulties
- Noisy breathing
Diagnosis:
- Medical history assessment
- Laryngoscopy to examine the airway
Treatment Options:
- Laser surgery combined with balloon dilation to widen the airway
- In severe cases, open airway reconstruction or resection of the narrowed segment may be required
Turbinate Reduction
Turbinate enlargement occurs due to chronic nasal allergies.
Diagnosis:
- Medical history assessment
- Nasal endoscopy
Treatment:
- Initial treatment with medications
- If symptoms persist, turbinate reduction surgery is performed
- Regular follow-up visits are required
Treatment of Nasal Fractures
Diagnosis:
- Medical history assessment
- Imaging (X-rays or CT scan)
Treatment:
- Fracture reduction can be performed under local anesthesia in the clinic or under general anesthesia in the operating room
- The patient requires at least two follow-up visits after the procedure
Treatment of Nosebleeds (Epistaxis)
Causes:
- A common cause is an injury or trauma to the small blood vessels in the nasal lining
- If no clear source is identified, a CT scan may be required to determine the cause
- In some cases, nosebleeds may be linked to blood pressure issues or clotting disorders
Treatment:
- In the clinic, treatment options include cauterization of the blood vessels or nasal packing for 48 hours in cases of severe bleeding
Ear Ventilation Tube Insertion
- This procedure helps drain accumulated fluid in the middle ear or prevent fluid buildup. The tubes allow air to flow in and out of the middle ear, balancing pressure and preventing fluid retention.
- Small plastic tubes are inserted through the eardrum, and they naturally fall out on their own within 6 to 18 months.
- For children, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia as a same-day surgery, while for adults, it can be done in the clinic under local anesthesia.
- Follow-up appointments with the doctor are scheduled within 2 to 4 weeks after surgery to check the tube’s position and function.
- Hearing improvement can be immediate if fluid buildup was the cause, but in cases of speech or learning difficulties, improvement may take several weeks or months.
Ear Ventilation Tube Insertion
This procedure is performed to drain accumulated fluid in the middle ear or to prevent fluid buildup. The tubes allow airflow to and from the middle ear, helping to balance pressure and prevent further fluid accumulation.
Treatment involves placing small plastic tubes through the eardrum, which naturally fall out on their own within 6 to 18 months.
For children, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia as a same-day surgery, while for adults, it can be done in the clinic under local anesthesia.
Follow-up appointments are scheduled within 2 to 4 weeks after surgery to check the tube’s position and function.
Hearing improvement may be immediate if fluid buildup was the cause. However, if the patient had speech or learning difficulties, improvement may take several weeks or months.
Adenoidectomy in Children
- Curettage (scraping) is used for thorough adenoid removal
- Thermal suction allows for quick adenoid removal, reducing surgery time, anesthesia duration, and bleeding risk
- The new Coblation technique minimizes pain, causes less bleeding, and shortens the procedure time
Treatment of Peritonsillar Abscess
- A peritonsillar abscess is a bacterial infection that develops due to untreated strep throat or tonsillitis, forming a pus-filled pocket near one of the tonsils
- Treatment involves draining the pus under local anesthesia and administering antibiotics and pain relievers
- In severe cases, an incision is made to drain the abscess in the operating room under general anesthesia, followed by antibiotic treatment
- Tonsillectomy may be required after recovery
Tongue-Tie Release and Treatment
- Tongue-tie (ankyloglossia) is a congenital condition that restricts tongue movement
- The release procedure can be performed in the clinic or under general anesthesia in the operating room
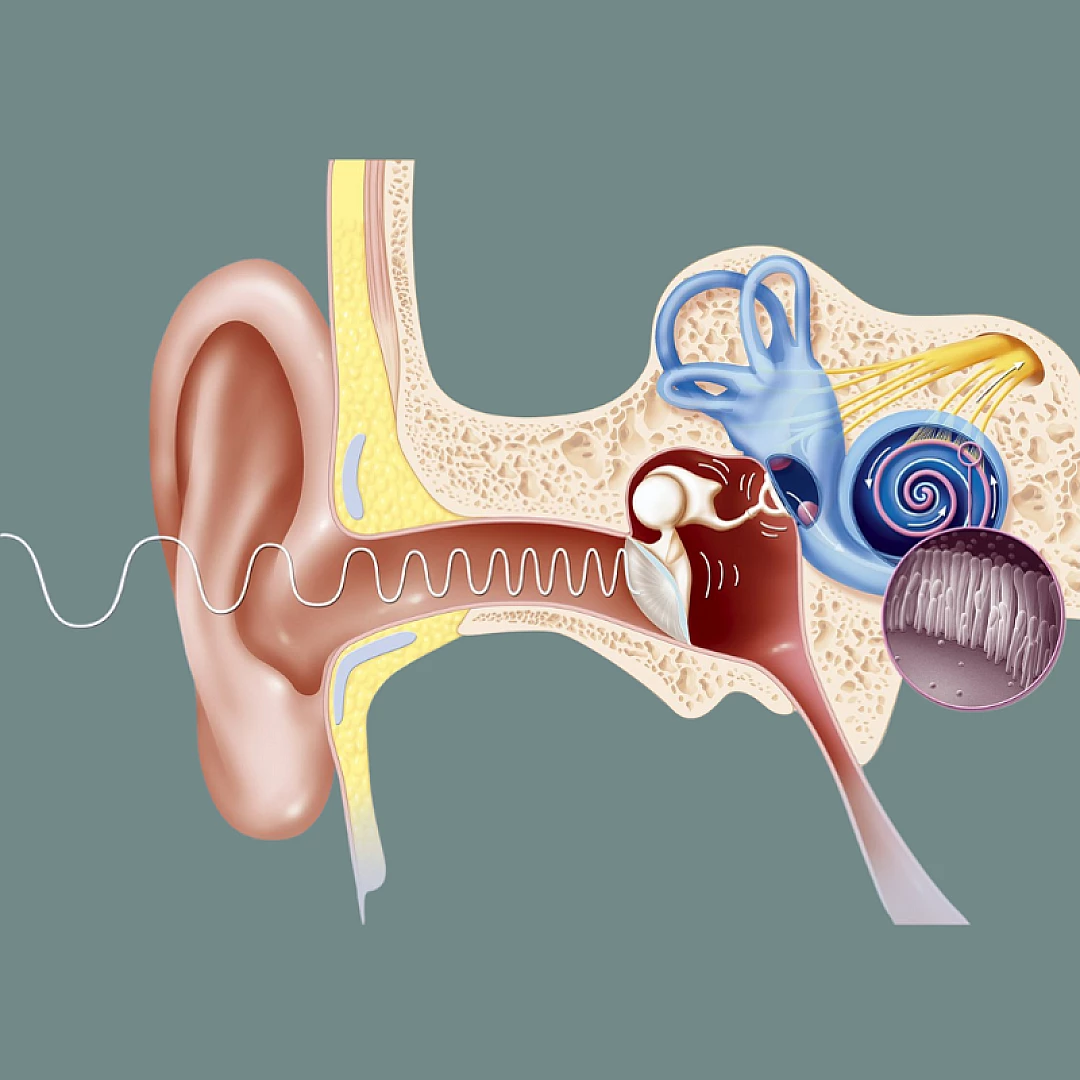
Hearing Problems
Diagnosis and Treatment
Treatment depends on the cause and severity of hearing loss.
Available treatments include:
- Wax Removal: Treatable blockages can be removed using suction or a small looped instrument
- Surgical Procedures: Used for conditions affecting the eardrum or hearing bones
- Hearing Aids: Beneficial for sensorineural hearing loss
Removing the Treatable Calcologenic Conditioner or using a small tool that has a loop at its end Surgical procedures: This includes eardrum distortions or hearing bones.
Sleep Disorders
Diagnosis and Treatment
Symptoms of Sleep Disorders:
- Feeling fatigued and exhausted
- Difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- Frequent awakenings after a short sleep duration
- Resisting sleep until late at night
- Excessive daytime sleepiness and low energy levels
- Difficulty concentrating and remembering
Diagnosis:
- Medical history assessment and physical examination
- Nasal and throat endoscopy
- Sleep study (polysomnography) if needed
Treatment:
- Depends on addressing the underlying cause
Other Treatments
- Sinus surgery using endoscopic techniques or medication treatment
- Tonsillectomy for both adults and children
- Diagnosis and treatment of laryngeal injuries
- Diagnosis and treatment of dizziness
- Diagnosis and treatment of sinus problems
- Diagnosis and treatment of nasal allergies
- Diagnosis and treatment of ear infections
- Diagnosis and treatment of swallowing difficulties
- Diagnosis and treatment of nasal obstruction
- Septoplasty (nasal septum surgery)
- Sinus surgery (endoscopic sinus surgery)
- Treatment of nasal polyps